What is Audio Forensics?
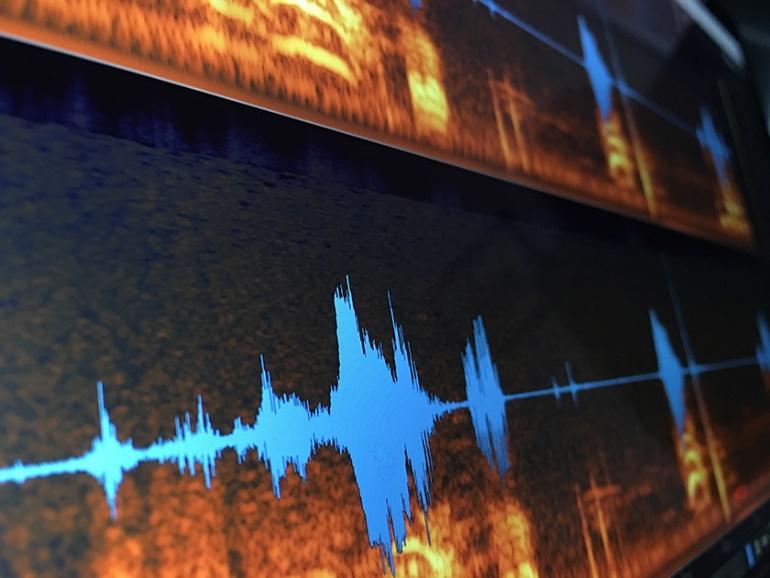

Audio forensics is a discipline of forensic science related to the acquisition, processing, and interpretation of recordings that may be used as evidence in a court of law.
Checking the authenticity, enhancing audio clarity, transcription of the audio, and audio comparison are all part of this examination.
Audio forensics evidence may be obtained from a tape recorder, cassette tapes, call center recordings or law enforcement agencies, surveillance tape recordings, telephone answering machines, voicemail recordings, and video cameras.
Types of Audio Forensic Investigations
Audio forensics includes authentication, enhancement, and interpretation.
Authenticity
In audio forensic investigations, one of the common requirements is to determine the authenticity of audio or recording. This confirms involves the recording’s integrity as well as verifying that the audio’s content is what it claimed to be.
If the sound or an audio recording changes abruptly. This indicates that the surrounding where the audio is being recorded change suddenly.
Enhancement
Many times, audio quality may be compromised by background noise, distortion, poor echo, many times vibrations, etc. In enhancement noise from the recorded audio or extracted audio reduces and the clarity of audio increases so that accurate transcription of audio is possible.
Interpretation
To determine its relevance and value to the investigations, the audio evidence for testing must be examined and interpreted.
Audio Enhancement Techniques
There are many techniques used to enhance the quality of audio.
- Critical Listening-Critical listening should be used by the forensic expert to start the enhancing process. Before applying any processing to the audio, they should listen to the tape many times and take notes on any alterations or faults they find. When addressing flaws in the recording, they note different areas of the audio and then mark these places.
- Electronic Measurements- After critical listening, the expert then uses electronic measurements to further examine the audio. This is done by noting different frequencies and different levels of recording. Spectrogram helps here in providing such information regarding frequencies.
If the frequency range suddenly becomes high or low, then this indicates there can be some editing performed. The development of new background noise or rapid changes in the background noise also implies that there is some editing.
- Visual Inspection-Inspecting the audio visually on the spectrogram is the next step in the audio enhancement techniques. If on examination there is some sudden break found in the waveform of audio, there should be some editing.
- Compression-In compression, very light or not easily heard sounds can be made audible by compressing the signal so that the amplitude of the sounds is reduced, and this will in turn make the least heard audio more audible.
What is a Spectrogram? A spectrogram is a visual representation of signal strength, or “loudness,” across time at different frequencies included in a waveform.
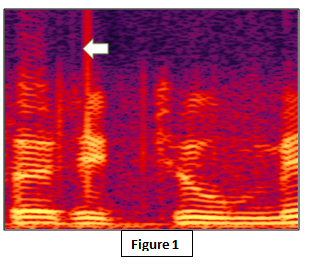
Fig. 1 from an audio spectrogram may reveal discontinuities in the sample audio. In this, a section of the digital audio recording was abruptly edited, resulting in a section represented by an arrow.
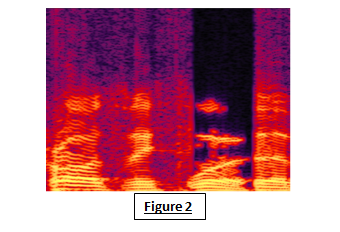
Fig. 2 from an audio spectrogram shows that some insertion of extra words takes place. This insertion can be easily detected by the change in the background noise visible in the spectrogram.
Report Preparation- the last step in this is the report prepared based on the evaluation of audio whether that audio is authentic or altered.
This content is meant for information only and should not be considered as an advice or legal opinion, or otherwise. AKGVG & Associates does not intend to advertise its services through this.
Posted by
Mansi Seewal (Forensic)
AKGVG & Associates

